Baker Pass
| Trail Features: | Outstanding Panoramic Views |  |
|||
| Trail Location: | Bowen/Baker Trailhead | ||||
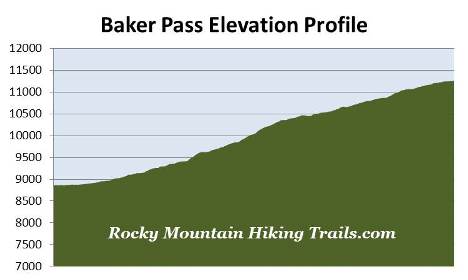
| Roundtrip Length: | 12.1 Miles | ||||
| Trailhead Elevation: | 8860 Feet | ||||
| Total Elevation Gain: | 2400 Feet | ||||
| Avg. Elev Gain / Mile: | 397 Feet | ||||
| Highest Elevation: | 11,253 Feet | ||||
| Trail Difficulty Rating: | 16.90 (strenuous) | ||||
| Parking Lot Latitude | 40.35486 | ||||
| Parking Lot Longitude | -105.85767 | ||||
Trail Description:
The hike to Baker Pass begins from the Bowen/Baker Trailhead, located 6.1 miles north of the Grand Lake Entrance. Although the hike starts in Rocky Mountain National Park, most of the route travels through the Never Summer Wilderness of the Arapaho National Forest.
The hike begins by crossing over the Colorado River, and then proceeds to travel across the Kawuneeche Valley along a gravel road. This valley is prime habitat for elk and moose, especially near the river and surrounding wetlands where sightings are fairly common. Both the Ute and Arapaho Indians used the Kawuneeche Valley as a summer hunting ground.
After walking about a quarter-of-a-mile hikers will reach the western edge of the meadow. Just past the tree line you'll notice a sign that reads "Baker Gulch / Bowen Gulch Trailhead to the left". Simply continue on the gravel road at this point. At just over one-third of a mile you'll reach a gate blocking the road. The Bowen Gulch Trail continues past the gate, while the Baker Gulch Trail branches off to the right. Hikers should turn right at this junction to continue towards Baker Pass.
At roughly three-quarters of a mile you'll exit Rocky Mountain National Park and enter the Never Summer Wilderness of the Arapaho National Forest. At the boundary is a kiosk to register your party, which is always a good idea in case you were to ever become lost or injured.
 The Never Summer Wilderness receives its name as a result of it being located within the Never Summer Mountains. The Arapaho Indians called these mountains "Ni-chebe-chii", which translates into “Never No Summer”. Wishing to avoid the use of a double negative, the U.S. Department of the Interior's Board on Geographic Names settled on Never Summer Mountains. Prior to its official naming, the mountains were known as the Rabbit Ear Range.
The Never Summer Wilderness receives its name as a result of it being located within the Never Summer Mountains. The Arapaho Indians called these mountains "Ni-chebe-chii", which translates into “Never No Summer”. Wishing to avoid the use of a double negative, the U.S. Department of the Interior's Board on Geographic Names settled on Never Summer Mountains. Prior to its official naming, the mountains were known as the Rabbit Ear Range.
During the early portions of the hike the trail travels over mostly easy to moderate terrain, while passing through dense lodgepole pine forest. At roughly 3 miles the trail enters a fairly large boulder field where the route becomes a little more rugged. The terrain also begins to open up here, with views of Peak 12,442 almost straight ahead. Hikers will likely notice many aspens throughout this section. As you pass through this area you should also keep an eye out for scraps of old rusted equipment, presumably remnants from the mining era.
 At just over 3.4 miles hikers will reach the Grand Ditch, an irrigation canal that diverts water from the Never Summer Mountains, over the Continental Divide, and into the Cache La Poudre River where farmers on the eastern plains use the precious commodity for crops. Begun in 1890, and completed in 1936, the ditch runs for 15 miles and diverts between 20% and 40% of the runoff from the Never Summer Mountains.
At just over 3.4 miles hikers will reach the Grand Ditch, an irrigation canal that diverts water from the Never Summer Mountains, over the Continental Divide, and into the Cache La Poudre River where farmers on the eastern plains use the precious commodity for crops. Begun in 1890, and completed in 1936, the ditch runs for 15 miles and diverts between 20% and 40% of the runoff from the Never Summer Mountains.
Paralleling the ditch is a service road. Hikers should turn left onto this road and walk about 100 feet to reach a rickety footbridge that crosses over the Grand Ditch. Once across the footbridge you should veer towards the right to continue along the Baker Gulch Trail.
At 4 miles hikers will cross over a stream without the benefit of a footbridge. During the late summer and fall months you shouldn't have any issues with this ford; however, during the spring run-off you'll likely get your feet wet. Shortly after crossing the creek you'll reach the Parika Lake Trail junction. To continue towards Baker Pass hikers should turn right here to proceed northbound along the Baker Gulch Trail.
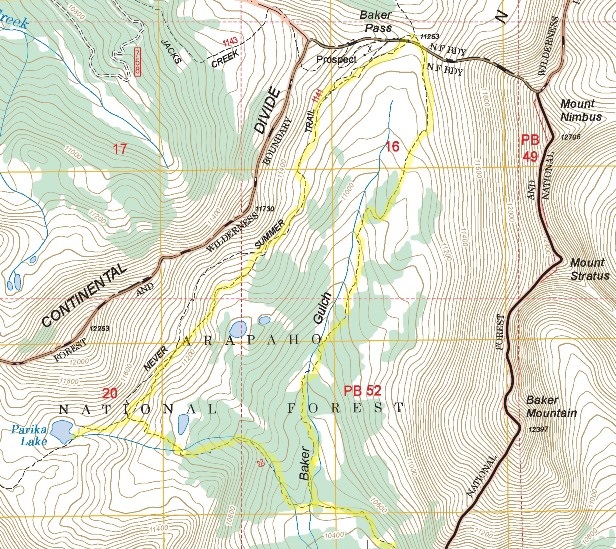
Over the course of the next mile-and-a-half the trail travels up Baker Gulch, while passing in and out of wooded areas. In some places the path is rather faint, and can be a little difficult to follow in some cases. This segment also travels over several boggy areas. Even in late-September our boots got a little muddy. During the early summer it's even worse, which could force hikers to move towards higher ground. If forced off the trail because it's too wet, or because you lost the trail, it's still fairly easy to find your own way towards the pass. This valley is fairly tight, with the stream on your left, and the steep mountain slopes on your right. Simply take the path of least resistance and proceed towards the north.
At roughly 5.5 miles the trail finally emerges from the canopy of the forest for the last time. From this point forward you'll enjoy spectacular views of alpine meadows and the surrounding mountains. The trail continues for another hundred yards to reach the top of a rise before you're able to see Baker Pass, the low point on the saddle straight ahead. Rather than making a beeline for the pass from this spot, the trail skirts towards the right in order to move to higher ground. During this stretch the trail becomes a little faint in some areas, but cairns have been built to help guide the way.

At just over 6 miles from the trailhead you'll finally reach the top of Baker Pass, which is marked by a national forest signpost. From this perch you'll enjoy spectacular 360-degree views. Towards the north, looking from left to right is Peak 12,098, Mt. Cirrus, Howard Mountain and 12,725-foot Mt. Cumulus, which dominates the view towards the northeast.

Looking towards the south, Mt. Nimbus, Mt. Strata and Baker Mountain form the wall along the east side of Baker Gulch. Further south, beyond the gulch, is Bowen Mountain, Peak 12,442, and Fairview Mountain. The Continental Divide forms the west flank above Baker Gulch. Peering just above the other side of the Divide is 12,394-foot Parika Peak.

From the top of Baker Pass there are several trails that lead deeper into the wilderness. The South Fork Michigan Trail drops down into the valley north of Baker Pass, while the Jack Creek Trail climbs steeply to reach the Continental Divide along the west side of the pass. Hikers will also have the option of creating a loop hike by taking the Baker Pass Trail, which leads southwest from the pass, and heads towards Parika Lake. This option would add another 1.4 miles and another 225 feet of elevation gain to your overall hike. You can read more about this outstanding loop hike by clicking here.
Hikers should always be aware of lightning risk while hiking in the Rocky Mountains, especially at higher elevations. As a general rule of thumb you should plan to be off the higher elevations before noon in order to avoid the notorious afternoon thunderstorms that frequent the mountains during the summer months. Hikers should also be prepared for extreme sun exposure, wind, cool temperatures, and rapidly changing weather conditions while on the trail. Make sure you have the proper gear with you, and know what safety precautions you need to consider beforehand.